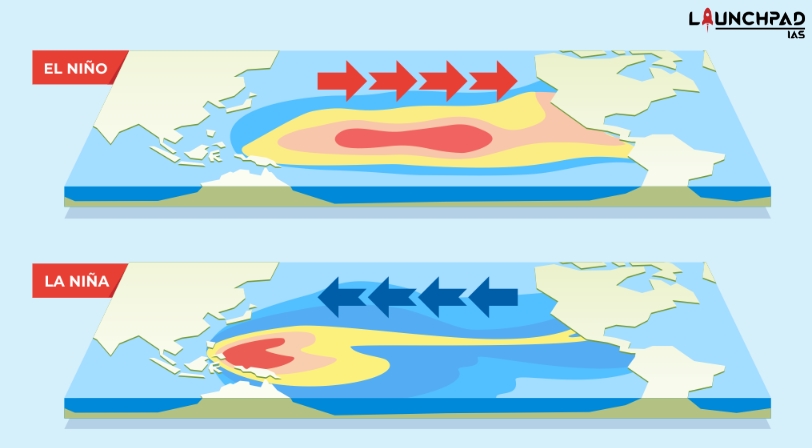
- EL Nino and La Nina are climate patterns in the Pacific Ocean that can affect weather worldwide.
- During normal conditions in the Pacific Ocean, trade winds blow west along the equator, taking warm water from South America towards Asia. To replace the warm water, Cold water rises from the depths of the Ocean – in a process called upwelling. EL Nino and LA Nina are two opposing climate patterns that break these Normal conditions.
- It is called the EL- Nino South Oscillation (ENSO Cycle)
- EL Nino and La Nina events two to seven years, on average but they do not occur on a regular schedule.
EL Nino
- EL Nino is Spanish and means “Little boy”
- It is a climate pattern that describes the usual warning of surface waters in the Eastern Tropical Pacific Ocean.
- It is the “warm phase” of a layer phenomenon called the EL – Nino Oscillation (ENSO)
LA Nina
- La Nina means “Little Girl” in Spanish.
- It is a pattern that describes the “usual cooling” of the tropical Eastern Pacific.
- La Nina may last between one and three years, which usually lasts no more than a year.
- It represents Below-Average sea surface temperatures across the East-Central equatorial Pacific.
- It is also associated with rainier-than-normal conditions over South Eastern Africa and Northern Brazil.
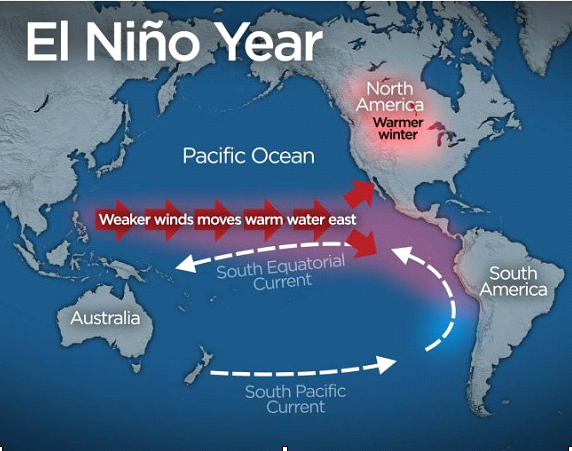
Impact of EL Nino
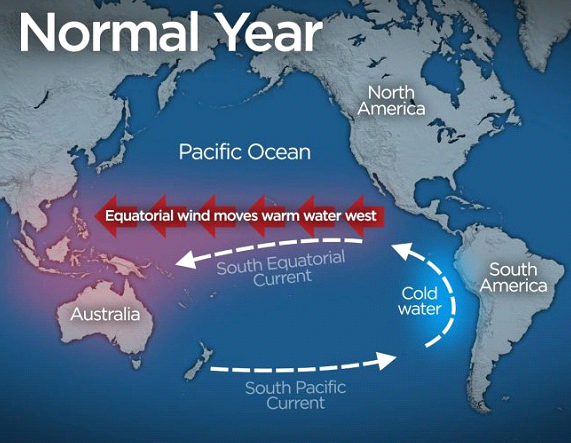
To understand the concept of El Nino, it’s important to be familiar with non-El Nino conditions in the Pacific Ocean.
- Normally, strong trade winds blow westward across the tropical Pacific, the region of the Pacific Ocean located between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn.
- Impact on Ocean: El Nino also impacts ocean temperatures, the speed and strength of ocean currents, the health of coastal fisheries, and local weather from Australia to South America and beyond.
- Increased Rainfall: Convection above warmer surface waters brings increased precipitation.
- Rainfall increases drastically in South America, contributing to coastal flooding and erosion.
- Diseases caused by Floods and Droughts: Diseases thrive in communities devastated by natural hazards such as floods or drought.
- El Nino-related flooding is associated with increases in cholera, dengue, and malaria in some parts of the world, while drought can lead to wildfires that create respiratory problems.
- Positive impact: It can sometimes have a positive impact too, for example, El Nino reduces the instances of hurricanes in the Atlantic.
- In South America: As El Nino brings rain to South America, it brings droughts to Indonesia and Australia.
- These droughts threaten the region’s water supplies, as reservoirs dry and rivers carry less water. Agriculture, which depends on water for irrigation, is also threatened.
- In Western Pacific: These winds push warm surface water towards the western Pacific, where it borders Asia and Australia.
- Due to the warm trade winds, the sea surface is normally about 0.5 meters higher and 4-5° F warmer in Indonesia than in Ecuador.
- The westward movement of warmer waters causes cooler waters to rise towards the surface on the coasts of Ecuador, Peru, and Chile. This process is known as upwelling.
- Upwelling elevates cold, nutrient-rich water to the euphotic zone, the upper layer of the ocean.
Impact of LA Nina
- Europe: In Europe, El Nino reduces the number of autumnal hurricanes.
- La Nina tends to lead to milder winters in Northern Europe (especially the UK) and colder winters in southern/western Europe leading to snow in the Mediterranean region.
- North America: It is continental North America where most of these conditions are felt. The wider effects include:
- Stronger winds along the equatorial region, especially in the Pacific.
- Favourable conditions for hurricanes in the Caribbean and central Atlantic area.
- Greater instances of tornados in various states of the US.
- South America: La Nina causes drought in the South American countries of Peru and Ecuador.
- It usually has a positive impact on the fishing industry of western South America.
- Western Pacific: In the western Pacific, La Nina increases the potential for landfall in those areas most vulnerable to their effects, especially in continental Asia and China.
- It also leads to heavy floods in Australia.
- There are increased temperatures in the Western Pacific, Indian Ocean and off the Somalian coast.
Also, check out :