History:
- The land boundary between Guyana and Venezuela has been disputed since its colonial inception between British and Spanish powers in South America.
- In the 1840s, the British government had the border unilaterally surveyed, but the proposed line encroached on Venezuelan territorial claims.
- The boundary has since been arbitrated (1899) and bilaterally agreed upon following demarcation (1905) but remains in conflict.
- While the British line, accepted by Guyana, is the current de facto boundary, Venezuela maintains a historic claim to all territory currently administered by Guyana west of the Essequibo River.
- Venezuelan contents that the Arbitral Award of 1899 about the frontier between British Guiana and Venezuela is null and void.
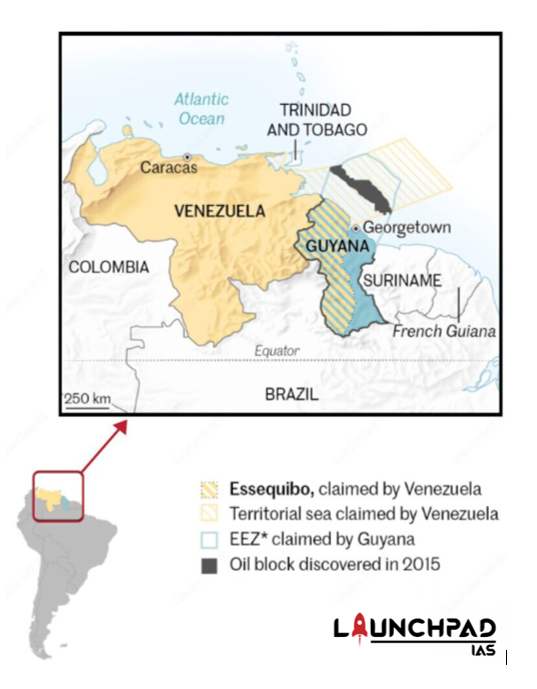
Disputed Area:
- Venezuela’s claim along the Essequibo River extends for 1,034 kilometers before reaching Brazilian territory.
- At stake is approximately 142,795 square kilometers that is currently administered by Guyana.
- Offshore the disputed land territory is maritime space that was recently discovered to be rich in hydrocarbon resources, upping the stakes of the land boundary dispute.
Current Status:
- Guyana submitted the dispute to the International Court of Justice in 2018.
- Despite Venezuela’s withdrawal from the case, proceedings are currently ongoing.
Guyana:
- Guyana is the world’s fastest-growing economy (GDP growth of 62.3% in 2022) and is on track to grow by more than 100% by 2028. The growth is largely fueled by profits from its oil production and export sector.
- It is a country on the northern mainland of South America.
- Guyana is an indigenous word that means “Land of Many Waters”.
- The capital city is Georgetown.
- It is the third-smallest sovereign state by area in mainland South America after Uruguay and Suriname.
- Bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north, Brazil to the south and southwest, Venezuela to the west, and Suriname to the east.
Venezuela:
- Venezuela has the world’s largest known oil reserves and has been one of the world’s leading exporters of oil.
- Capital and largest city- Caracas.
- Colonized by Spain in 1522.
- It was a part of the Republic of Colombia and separated as a full sovereign country in 1830.
Essequibo River
- Essequibo River, a river in east central Guyana, is the largest river between the Amazon and the Orinoco.
- It rises in the Acarai Mountains on the Brazilian border and flows northward for approximately 630 miles (1,010 km) through savannas and forests to the Atlantic Ocean.
- It reaches the Atlantic Ocean 13 miles (21 km) west-northwest of Georgetown, the national capital, of -Guyana.
- Its estuary, 20 miles (32 km) wide, is obstructed by islands and silt.
- With its chief tributaries, the Rupununi, Mazaruni, and Cuyuni, its system drains more than half of Guyana.
- The River is administered by Guyana. However, Venezuela has, for decades, laid claim to Essequibo.
- Venezuela has claimed that the Essequibo River to the region’s east forms a natural border and has historically been recognized as such.
Global Support:
- India, with diasporic ties, supports Guyana; the US also backs Guyana’s sovereignty.
Related Links: AUKUS