HPPSC conducts exams for various administrative posts in Himachal Pradesh State, to crack this exam candidates have to undergo a rigorous process. The HPPSC State Civil Services Exam is conducted in 3 stages.
First Stage: It is a preliminary objective-type paper, which consists of 2 parts: –
- General Studies
- Aptitude Test
The first stage is meant to serve as a screening test only. The marks obtained in the Preliminary Exam will not be counted for the final order of merit.
The Aptitude Test will be only Qualifying where a candidate has to qualify for this exam with 33% Marks. Marks obtained in this test will not be used for merit orders.
Note: There will be negative markings for every wrong answer. One Third of the marks assigned to that question will be deducted as a penalty.
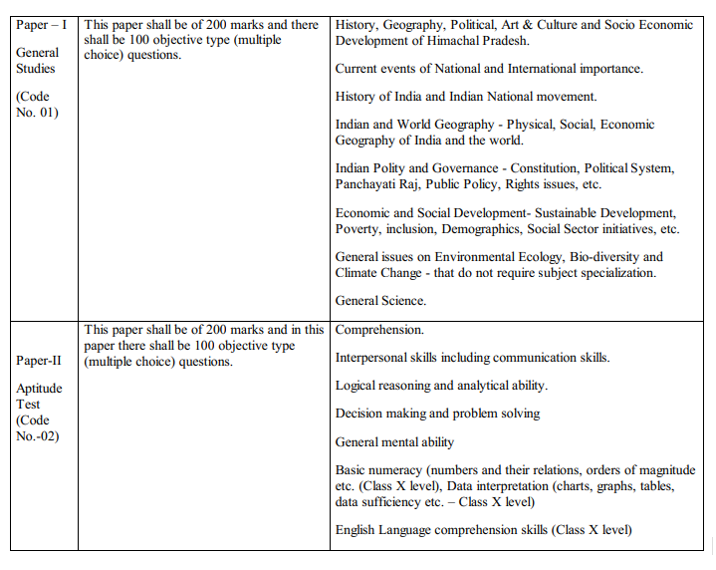
| Subject | No. of questions | Marks |
| GS | 100 | 200 |
| Aptitude Test | 100 | 200 |
Syllabus for Preliminary Examination
Second Stage: This stage consists of 6 compulsory papers (Subjective) and one optional subject.
| PAPERS | SUBJECTS | MARKS |
| Compulsory Paper 1 | English | 100 |
| Compulsory Paper 2 | Hindi | 100 |
| Essay Paper | Essay | 100 |
| Paper 1 | GS 1 | 200 |
| Paper 2 | GS 2 | 200 |
| Paper 3 | GS 3 | 200 |
No candidate Taking the Mains Exam will be considered to have qualified unless he/she obtains 40% marks in English and Hindi and 45% (aggregate) in the remaining papers. Every candidate has to opt for the Optional subject
| Optional Exam | Marks |
| Paper 1 | 100 |
| Paper 2 | 100 |
HPPSC HPAS Mains Syllabus 2024
| Subject | Topics |
| HPPSC HPAS English Paper-100 Marks | English Grammar – (20 Marks) Usage and Vocabulary – (20 Marks) English Composition Letter/ Application/ Report/ Note writing – (20 Marks) Comprehension of unseen passages – (20 Marks) Precis Writing – (20 Marks) |
| HPPSC HPSC Hindi Paper in Devnagri Script-100 Marks | Translation of an English passage into Hindi. Translation of Hindi passage into English. Explanation of Hindi passage in Prose and Poetry in the same language. Composition (Idioms, corrections, etc.) |
| HPPSC HPAS Essay Paper-100 Marks | A fair choice of topics covering Current affairs Socio-political issues Socioeconomic issues Aspects of culture and history and reflective topics. |
HPPSC HPAS Syllabus for General Studies I
Check the HPPSC HPAS mains syllabus for General Studies I tabulated below.
| HPPSC HPAS GS I Syllabus 2023 | |
| Unit One | Sub-Unit 1 Historical perspective of Indian Cultural heritage. Literature and Art forms from ancient times to 1947. Modern Indian history from mid–18th century till 1980. Freedom Struggle covers various stages and the role of eminent persons from different parts of India. Sub-Unit 2 Industrial Revolution and the Emergence of Capitalism. Fascist Ideology and its global implications. World Wars and boundary settlements after the First and the Second World Wars. Concepts of Decolonization, Nationalism and Socialism, Globalization, and Concept of Modernity. Sub Unit 3 Emergence and growth of early medieval states in HP: Kangra, Kullu, and Chamba. Hill States and their relations with the Mughals and the Sikhs. Gorkha invasion and consequences, Treaty of Sugauli. Political and Administrative structure under the Colonial power. Grants, Sanads, and territorial aggression. Socio-economic conditions under the colonial period with special reference to the social practices of Beth, Begar, and Reet. Establishment of British Cantonments. National Movement with special reference to Praja Mandal movements in Himachal Pradesh, 1848-1948. Five-Year Plans and Vision for the Hill State. Survey of artistic and cultural Heritage (Temples, Buddhist Monasteries, and Paintings) relevant to the State of Himachal Pradesh. Topics relevant to the State of Himachal Pradesh. |
| Unit Two | Sub Unit 1 Introduction to Disasters: Concepts, definitions, disaster classifications including natural and man-made disasters. Social and Environmental impacts of disasters. Disaster profile of the country. Approaches to Disaster Risk Reductions. Disaster management models. Roles and responsibilities of stakeholders including community, Concept of first responders. Interrelationship of disaster and development. Disaster management in India including Disaster Management ACT 2005, National and state policies, Plans, and institutional mechanisms in the country Sub Unit 2 Geographical Introduction to India, India as a unit of Geographical Study. Aspects of the Physical Geography of India – Structure and Relief, Climate, Soils and Vegetation, Geomorphic setup (Mountain Ranges and Rivers and other Water Bodies). Human Aspects – Population distribution, Urban Population, Internal Migration Language and Literacy, Villages and Towns in India. Settlements, Industry and Transport. Sub Unit-3 Geography of Himachal Pradesh: Relief, Drainage, Vegetation cover and types. Climate and climatic zones in Himachal Pradesh. Geographical Regions of Himachal Pradesh (Shiwalik, Doons and Low Valleys, Outer Valleys of Sub Himalaya, Mid Hill Tracts of High Himalaya, High hills and Valleys and Inner Zones). Human Aspects: Quantitative, Qualitative and Temporal characteristics of Population, Urbanisation pattern. Policies: Forest, Industrial, and Tourism Policies, Growth of Industrial areas and types of Industries in Himachal, Employment generation and potential, Scope of future Industrialization, Hazard Vulnerability and Risk Profile of Himachal Pradesh |
HPPSC HPAS Syllabus for General Studies II
Check the HPPSC HPAS mains syllabus for General Studies II tabulated below.
| HPPSC HPAS Syllabus for GS Paper II | |
| Unit One | The Constitution of India covering Historical underpinning, evolution, and salient features. Significant provisions include Fundamental Rights, Directive Principles of State Policy, and Fundamental Duties. Amending process and important Constitutional Amendments and theory of basic structure. Parliament and State legislatures and functioning of the Union and State Executive and the Judiciary. Functions and responsibilities of Union and States. Issues and challenges of the federal structure, devolution of powers and finances up to local level and challenges therein. Salient features of the Representation of People’s Act. Appointments to various constitutional posts, powers, functions, and responsibilities of various constitutional bodies in India. Reorganization and politics of statehood. Development of political parties, major Political parties, and their support base and performance in the Assembly and Parliamentary elections in Himachal Pradesh. Politics of sub-regionalism and pressure groups in the State. Structure, organization, and functioning of Statutory, Regulatory, and various Quasi-Judicial bodies in Himachal Pradesh. |
| Unit Two | Institutional framework development in various sectors in India. Governance, Good governance, Citizen Charters, effective public service delivery, transparency, accountability, and ethics in governance in India. District Administration: The changing role of Deputy Commissioner. Local self-government in urban and rural areas in India. Role of Non-Government Organizations (NGOs). Self Help Groups (SHGs) and Civil Society in Governance in India. Bodies constituted Policies, Programmes, and Schemes for the welfare of Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, Women, Minorities, Backward classes, Differently-abled persons, and children in India. Issues relating to the quality of life cover livelihood, poverty, hunger, disease, and social inclusiveness. Governance in Himachal Pradesh. The Himachal Pradesh Public Service Guarantee Act 2011. Right to Information Act, 2005, and rules made thereunder by the Himachal Pradesh Government. Administrative reforms for effective public service delivery in Himachal Pradesh. Implementation of 73rd& 74th Constitutional amendments in Himachal Pradesh. Issues and Challenges, Programmes and Policies for the welfare of differently-abled persons, women and children in Himachal Pradesh. |
| Unit Three | Bilateral, Regional, and Global groupings and agreements involving India and affecting India’s interests. India’s Look East policy. India’s relations with the United States of America (U.S.A.), Russia, China, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Afghanistan, Nepal, Maldives, and Middle Eastern countries. Effects of the policies of developed and developing countries on India’s interest, Indian Diaspora. Important international Institutions. Cybercrime and drug menace & mechanism to detect and control it in Himachal Pradesh. Enactments made by Himachal Pradesh Government to protect and promote the interests of agrarian society. Various policies were framed by the Government of Himachal Pradesh for the socioeconomic development of Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes of the State. Tribal welfare administration, Tribal sub-plan, and Single line administration in Himachal Pradesh. |
HPPSC HPAS Syllabus for General Studies III
Check the HPPSC HPAS mains syllabus for General Studies III tabulated below.
| HPPSC HPAS GS III Syllabus | |
| Unit I | |
| Sub Unit–1 | Characteristics of Indian Economy: Demographic Profile, Demographic Dividend, and Population Policy. Sectoral Composition with respect to contribution to Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and Employment. Poverty and Inequality, Unemployment, Inflation in India. Industrial Growth in India. Regulatory framework for money and banking: Reserve Bank of India (RBI), Commercial banks and Regional Rural Banks. Monetary policy, Foreign exchange, Balance of Payment Scenario. Foreign Trade: Policy, Composition and Direction, Impact of Liberalization / Privatization and Globalization. |
| Sub Unit 2 | Economic Planning in India. Five Year Plans: strategies and outcomes, Public / Private / Joint Sectors. Fiscal Policy, Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management Act, 2003, Debt and Investment in India: Current Status, Growth and Development experience including Natural Resource Management. Sustainable development and Inclusive growth. Measurement of economic development: Physical Quality of Life Index (PQLI), Millennium Development Goals, Human Development Index (HDI) / Gender Development Index (GDI) / Gender Empowerment Measure (GEM). Latest / Current Development Schemes / Initiatives / Institutional Changes (e.g. Swach Bharat Mission, Make in India, Digital India, Skill India, Sansad Adarsh Gram Yojana, Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS), National Institution for Transforming India (NITI) Ayog etc. International Financial and Economic Organizations: International Monetary Fund (IMF), World Trade Organization (WTO), International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD), International Development Association (IDA), United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa (BRICS). |
| Sub Unit 3 | Economy of Himachal Pradesh: Demographic profile and Human resource, Sectoral distribution of Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP). Diversification in Agriculture and allied activities, Land tenure, and size of land holdings. Industrialization in the state. Skilled / Unskilled labor. Revenue generation with special reference to hydro potential, tourism, flora, and fauna. Cottage and Small Scale Industries. Tax base, Pros and Cons of Special Category status. Appraisal of education, Health, Physical, and Financial Infrastructure Development. |
| UNIT-II | |
| Sub Unit-1 | Applications of space technology in natural resources, development, and communications. Important missions and programs of the Department of Space and Indian Space Research Organization. Historical evolution of the Indian Space program. Lunar, interplanetary, and Earth Observation Missions. Remote Sensing and Communication satellites. Applications of Remote sensing and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) for natural resources monitoring and applications benefiting the common man. |
| Sub Unit 2 | Developments in energy sectors such as Hydropower, nonconventional sources of energy, and nuclear energy include policies, programs, and research bases in the country. Concepts of nonconventional, renewable, clean, and environment-friendly energy sources. Role of energy in sustainable development. |
| Sub Unit 3 | Modern and emerging technologies and initiatives in the State of Himachal Pradesh including biotechnology policy, research, vision, scope, and applications for developing horticulture, medicinal, and aromatic plant resources of the State. IT policy of Himachal Pradesh and its role in governance, the concept of Himachal State Wide Area Network (HIMSWAN), State plans of e-governance, the concept of LokMitra Kendra and Aryabhatta Geo-Informatics Space Application Centre (AGISAC). State Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan. Endangered and threatened species of Himachal Pradesh. Factors responsible for Biodiversity decline in Himachal Pradesh. Relevance and role of Intellectual Property Rights, Geographical Indications, and Traditional wisdom and knowledge in the sustainable development of the State. |
| Unit-III | |
| Sub Unit-1 | Issues, concerns, policies, programs, conventions, treaties, and missions aimed at environment protection, and dealing with the problem of climate change. State of environment reports. Environment protection and pollution control Act and rules. Environment Impact Assessment. National Action Plans on Climate Change. Himalayan ecology, biosphere reserve, Science and economics of climate change. Social and ethical issues in the use of Biotechnology. |
| Sub Unit-2 | Latest developments in science and technology for harnessing agriculture, horticulture, medicinal, and herbal resources in the country. National mission for sustainable agriculture, mission for integrated development of horticulture. Concept of organic farming, seed certification, rainwater harvesting, techniques of irrigation and soil conservation, and soil health cards. |
| Sub Unit-3 | Tourism policy, potential and initiative in Himachal Pradesh. Types of tourism: religious, adventure, heritage, Important tourist destinations in Himachal Pradesh. Social, Economic, and Cultural implications of Tourism. Concept of Eco-Tourism and green tourism and their role in sustainable development of the State. Environmental concerns of the tourism industry, both positive and negative effects including climate change regarding Himachal Pradesh |
Third Stage: The third stage is the Interview or Personality stage. In this, the five-member board will judge the mental caliber of candidates and also ask questions relating to the knowledge and customs of Himachal Pradesh.
Marks obtained by the candidates in the (Preliminary) Examination will not be counted for the purpose of a final order of merit. However, marks obtained in the main examination as well as in the Personality Test would determine their final merit for selection. The marks obtained in the Compulsory Papers in English and Hindi will not be counted for the overall ranking.
In the event of a tie, the order of merit shall be determined in accordance with the highest marks secured in the interview/ Personality Test and if the marks in the Interview / Personality Test are also equal, then the order of merit shall be decided in accordance with the highest marks obtained by such candidates in the aggregate of the compulsory subjects (excluding English and Hindi Paper) and if the marks in the aggregate of the compulsory subjects are also equal, then the order of merit shall be decided in accordance with the highest marks obtained by such candidates in the Essay Paper and in case there is still a tie, then the elder candidate shall be placed higher in the merit.
Related Links: UPSC SYLLABUS