What Led to Instability in Myanmar?
- Background – The country gained independence from Britain in 1948. It was ruled by the armed forces from 1962 until 2011, when a new government began ushering in a return to civilian rule.
- In the 2010s, the military regime decided to transition the country towards democracy. Although the armed forces remained powerful, political opponents were freed and elections were allowed to be held.
- The National League for Democracy won the 2015 election, the country’s first free and fair election participated by multiple parties, and formed the government, raising hopes that the country is on its way to a full transition to democracy.
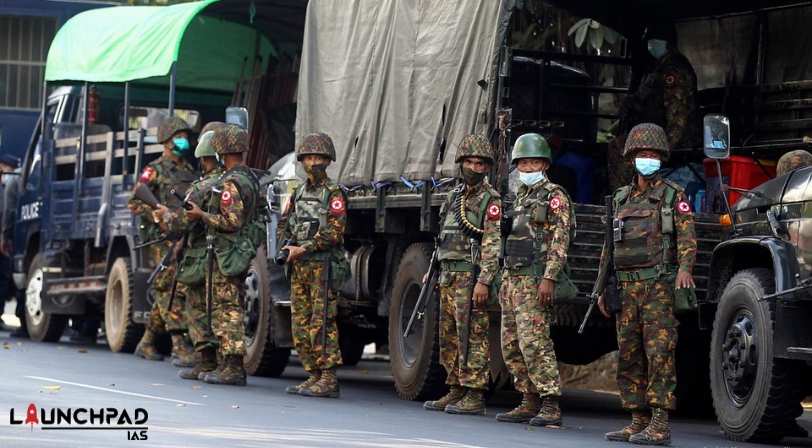
Military Coup:
- In the November 2020 parliamentary election, NLD secured the majority of the seats.
- The 2008 military-drafted constitution allocates 25% of the total seats in Myanmar’s Parliament to the military, and it also designates several key ministerial positions for military appointees.
- When the newly elected Myanmar lawmakers were to hold the first session of Parliament in 2021, the military imposed a state of emergency for one year citing massive voting fraud in the parliamentary elections.
Associated Issues Highlighted by UN:
- Despite clear legal obligations for the military to protect civilians in the conduct of hostilities, there has been consistent disregard for the related rules of international law.
- Myanmar’s economy has collapsed with nearly half of the population now living below the poverty line.
- Since launching the coup, the military has imprisoned the democratically elected leadership of the country and, in subsequent months, detained over 16,000 others.
The Rohingya Issue:
- On August 25, 2017, an outbreak of violence in Myanmar’s Rakhine State forced hundreds of thousands of Rohingya people to flee their homes.
- The pro-democracy movement in Myanmar has also cut off the Rohingya community.
- Over the years, the pro-democracy movement in Myanmar has faced various challenges, including restrictions on freedom of speech and assembly, arbitrary arrests and detentions, censorship, and violence.
- In January 2020, the UN’s top court (ICJ) ordered Myanmar to take measures to protect members of its Rohingya community from genocide.
What is India’s Stand on Myanmar Issue?
- In recent years, India has expressed concerns over the human rights situation in Myanmar, particularly with regard to the Rohingya crisis.
- India has called for peaceful resolution of the issue, respect for human rights, and accountability for those responsible for human rights violations.
- Though India has expressed deep concern over recent developments in Myanmar, cutting off from the Myanmar military is not a viable option as India has significant economic and strategic interests in Myanmar and its neighbourhood.
- India’s stance on the issue of Myanmar may evolve based on the evolving situation and geopolitical dynamics in the region.
You can read more such blogs on our website https://launchpadeducation.in/current-affairs/


