About:
- Ramsar Convention is a convention on wetlands that was signed in 1971 in the Iranian city of Ramsar.
- The negotiations for the convention started in the 1960s by the different countries and NGOs for the protection of wetlands and their resources. Finally, it came into force in 1975.
Aim :
To conserve and use wisely all wetlands through local and national actions and international cooperation, as a contribution towards achieving sustainable development throughout the world.
Three pillars of the Ramsar Convention are:
- Designation of wetlands of international importance as Ramsar Sites;
- Promotion of the wise use of all wetlands in the territory of each country; and
- International cooperation with other countries to further the wise use of wetlands and their resources.
What are Wetlands?
- According to Article 1 of the Ramsar Convention, wetlands are defined as “areas of marsh, fen, peat, and or water, whether natural or artificial, permanent or temporary, with water that is static or flowing, fresh, brackish or salt, including areas of marine water the depth of which at low tide does not exceed six meters.”
- Wetlands thus include the following:
- marine—coastal wetlands such as coastal lagoons, rocky shores, and coral reefs
- estuarine—for example, deltas, tidal marshes, and mangrove swamps
- lacustrine—wetlands associated with lakes
- riverine—wetlands along rivers and streams
- palustrine—marshes, swamps, and bogs
- human-made wetlands such as reservoirs, fish ponds, flooded mineral workings, saltpans, sewage farms, and canals.
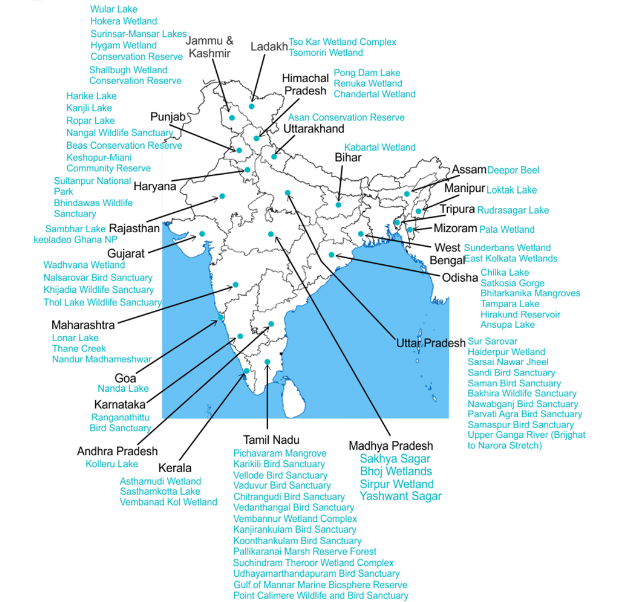
India and Ramsar Convention
India became a party to the convention on February 1, 1982. Between 1982 to 2013, 26 Ramsar sites were added to the list by India. The number has only increased in recent years totaling around 75 today.
What are Ramsar Sites?
- Ramsar sites are wetland sites of international importance under the “Convention on Wetlands”.
- Globally, there are over 2400 Ramsar sites.
- The largest number of sites are located in the United Kingdom followed by Mexico.
The Montreux Record
- The Montreux Record is a register of wetland sites on the List of Wetlands of International Importance where changes in ecological character have occurred, are occurring, or are likely to occur as a result of technological developments, pollution, or other human interference. It is maintained as part of the Ramsar List.
- The Montreux Record was established by the Recommendation of the Conference of the Contracting Parties (1990).
- Sites may be added to and removed from the Record only with the approval of the Contracting Parties in which they lie.
Criteria:
One of the nine criteria must be fulfilled to be the Ramsar Site.
- Criterion 1: If it contains a representative, rare, or unique example of a natural or near-natural wetland type found within the appropriate biogeographic region.
- Criterion 2: If it supports vulnerable, endangered, or critically endangered species or threatened ecological communities.
- Criterion 3: If it supports populations of plant and/or animal species important for maintaining the biological diversity of a particular biogeographic region.
- Criterion 4: If it supports plant and/or animal species at a critical stage in their life cycles, or provides refuge during adverse conditions.
- Criterion 5: If it regularly supports 20,000 or more waterbirds.
- Criterion 6: If it regularly supports 1% of the individuals in a population of one species or subspecies of waterbird.
- Criterion 7: If it supports a significant proportion of indigenous fish subspecies, species or families, life-history stages, species interactions, and/or populations that are representative of wetland benefits and/or values and thereby contribute to global biological diversity.
- Criterion 8: If it is an important source of food for fishes, spawning ground, nursery, and/or migration path on which fish stocks, either within the wetland or elsewhere, depend.
- Criterion 9: If it regularly supports 1% of the individuals in a population of one species or subspecies of wetland-dependent non-avian animal species.
Ramsar sites in India: